160 Views
Causes and Prevention of Shin Splints
The causes and prevention of shin splints or groin injury. A comprehensive guideline for groin injury, causes, treatment and prevention.
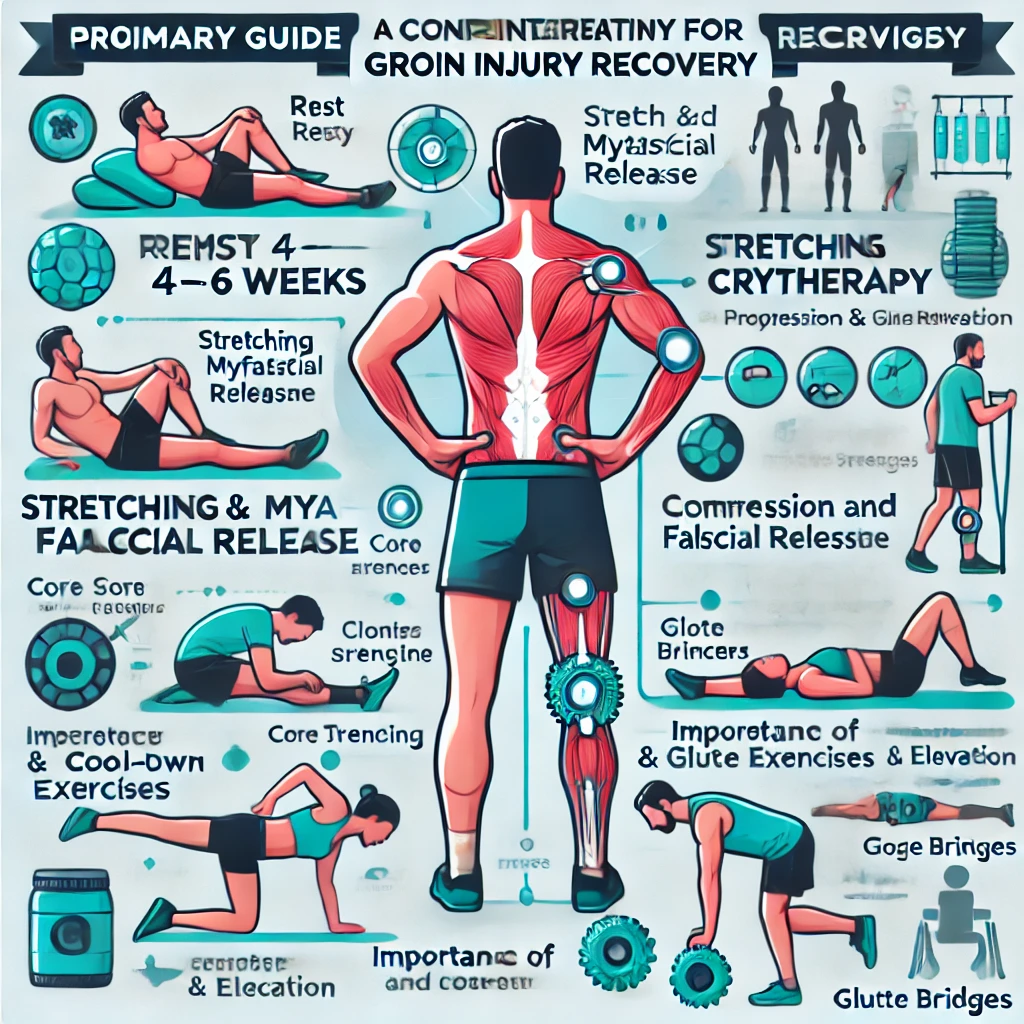
Primary Recovery Strategies:
- Rest (4–6 weeks) and Cryotherapy: It is crucial to refrain from activities that may exacerbate the injury. Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15–20 minutes, three to four times daily to minimise inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Stretching and Myofascial Release: Engaging in gentle stretching exercises and utilising a foam roller can effectively reduce muscle tension and enhance blood circulation, promoting a faster healing process.
- Compression and Elevation: The application of compression bandages can help manage swelling while elevating the injured limb, which assists in reducing fluid accumulation and accelerating recovery.
- Progressive Strengthening Exercises: Once pain and inflammation subside, gradually incorporate targeted strengthening exercises to restore muscle stability and function.
Additional Recovery Measures:
- Gradual Reintegration into Physical Activity: A structured return-to-sport plan should be implemented, beginning with low-intensity exercises and progressively increasing in intensity and complexity to prevent re-injury.
- Importance of Warm-Up and Cool-Down Routines: Adequate warm-up and cool-down exercises are essential in preparing the muscles for exertion and facilitating recovery post-activity, thereby reducing the likelihood of future injuries.
- Core and Glute Strengthening: Weakness in the core and gluteal muscles can contribute to groin injuries. It is beneficial to include targeted exercises aimed at strengthening these areas to enhance overall stability and reduce strain on the groin region.
Recommended Exercises for Groin Injury Rehabilitation:
- Leg Raises: Strengthens the hip flexors and improves muscle endurance.
- Lunges: Enhances lower body stability and mobility.
- Leg Press: Builds strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Calf Raises: Supports lower limb stability and coordination.
- Glute Bridges: Activates and strengthens the gluteal muscles, reducing stress on the groin.
- Planks: Develops core strength, which is crucial for overall stability and injury prevention.
By adhering to these recovery protocols, individuals can facilitate a safe and effective rehabilitation process, minimising the risk of recurrent injuries while optimising physical performance.